
Write with Integrity How to Avoid Plagiarism
July 23, 2025
To sidestep plagiarism, you have to know what you're looking for. It’s not just about blatant copy-pasting. The real strategy is a mix of solid research habits, meticulous citation of every single borrowed idea, and using tech as a final safety net. Once you get these practices down, you can be confident your work is original and stands on its own.
What Plagiarism Really Is And Why It Matters

At its heart, plagiarism is passing off someone else's work or ideas as your own. Whether you have their consent or not, if you use it in your own work without giving full credit, you’re crossing a line. It’s basically intellectual theft, and it chips away at the trust that holds all creative and academic work together.
Most people think it’s just copying a chunk of text. The reality is far more nuanced.
The fallout isn't just a slap on the wrist or a failing grade. In the professional world, plagiarism can get you fired, land you in legal trouble, and permanently stain your reputation. It shatters the trust between you and your audience—be it professors, clients, or readers. Originality isn't just a rule to follow; it's the currency of your credibility.
Exploring The Different Forms Of Plagiarism
The first real step to avoiding plagiarism is understanding all the different ways it can show up. Accidental plagiarism, for instance, is a big one. It happens when a writer honestly forgets a citation or paraphrases a bit too closely. The intent might not be malicious, but the consequences are often the same as deliberate cheating.
Then there’s the more subtle stuff, like mosaic plagiarism—sometimes called "patchwriting." This is where you weave phrases and sentences from a source into your own writing without using quotation marks. It creates a patchwork of original and borrowed content that, you guessed it, is still plagiarism.
Even reusing your own work without getting permission, known as self-plagiarism, can get you into hot water. For a deeper look at steering clear of these common pitfalls, check out these essential tips for avoiding plagiarism.
The bottom line with any form of plagiarism is the failure to give credit where it's due. It misrepresents where an idea came from and robs the original creator of their intellectual property.
To really get why this is such a big deal, it helps to know the legal side. Plagiarism often crosses over into copyright violation. Understanding the foundational differences between trademark and copyright really drives home why protecting intellectual work matters so much.
A Clear View Of Plagiarism Types
To make these ideas crystal clear, let's break down the most common types of plagiarism you'll run into. Spotting them in the wild is key to building good writing habits that stick.
This table gives you a simple look at what to watch out for.
Types of Plagiarism and How to Recognize Them
| Plagiarism Type | What It Is | A Quick Example |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Plagiarism | Copying text word-for-word from a source without using quotation marks or attribution. | Taking a sentence from a website and pasting it directly into your essay as if you wrote it. |
| Mosaic Plagiarism | Mixing your own words with phrases from a source without proper citation. | Swapping out a few words in a source's sentence with synonyms but keeping the original structure. |
| Self-Plagiarism | Reusing significant portions of your own previously submitted work without permission or citation. | Submitting a paper for one class that you already turned in for another class last semester. |
| Accidental Plagiarism | Unintentionally failing to cite a source, misquoting, or paraphrasing improperly. | Forgetting to add an in-text citation for a statistic you found during your research. |
Being familiar with these forms of plagiarism is half the battle. When you know what to look for, you're much less likely to make these mistakes yourself.
Building Your Defense Against Accidental Plagiarism
The best way to sidestep plagiarism isn't just about being extra careful—it's about building a rock-solid system that stops it before it even gets a chance to start. This means creating a workflow that, from day one, keeps your original thoughts completely separate from your source material. Honestly, it’s more about being organized than just being honest.
A huge part of this defense comes down to knowing how to organize research notes properly. Think about it: a messy research process, where you've got source quotes and your own brilliant ideas all jumbled up in the same document, is a recipe for disaster. The lines blur, and before you know it, you can’t remember if that killer insight was yours or something you skimmed in an article last week.
This infographic breaks down the most common ways people fall into the plagiarism trap. It’s a great visual for spotting risks in your own process.
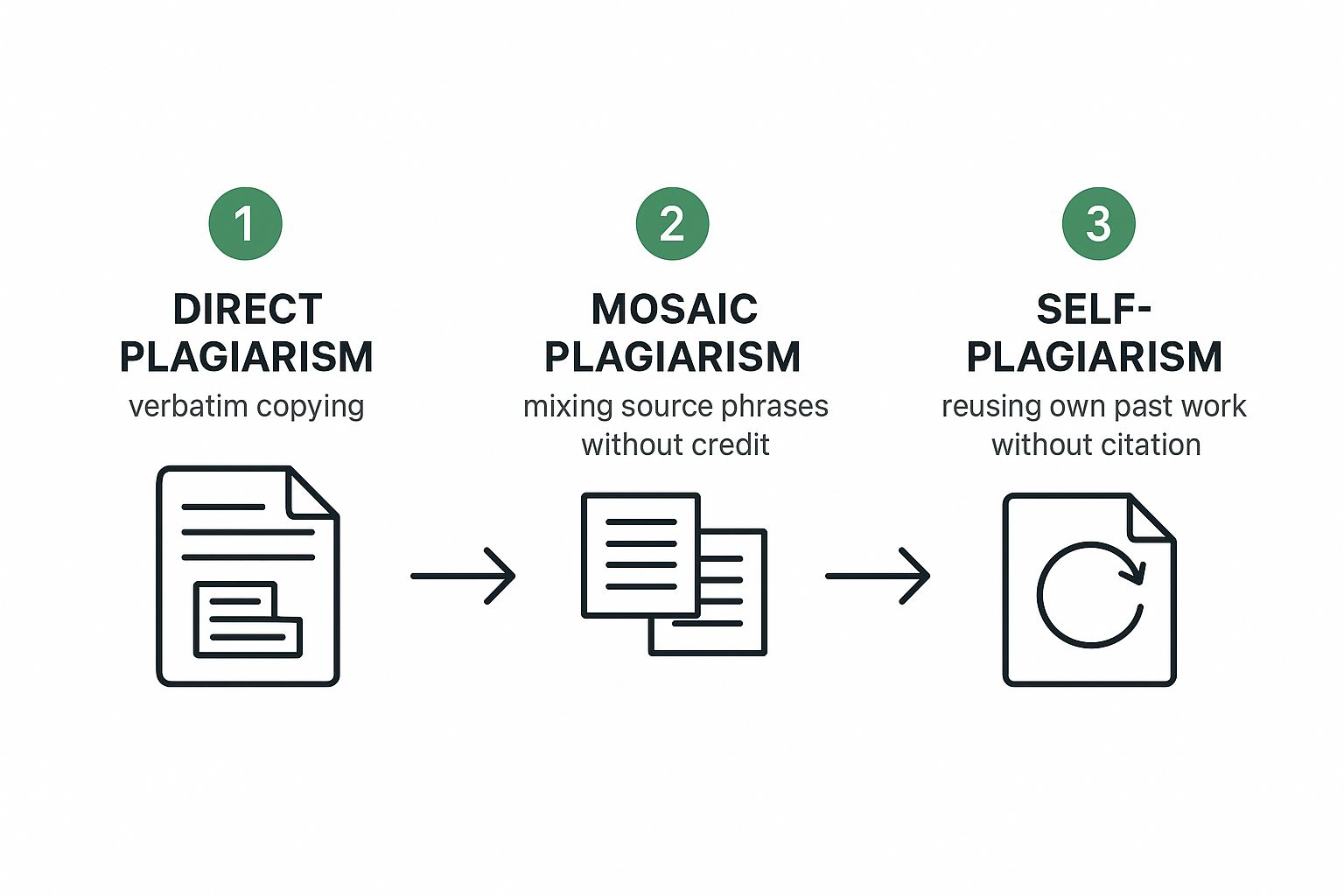
As you can see, whether it's blatant copying or subtle "patchwriting," the root cause is almost always the same: a failure to properly separate and credit outside material. A disciplined approach to note-taking is your best weapon against these common slip-ups.
The Quote-Paraphrase-Summary Method
I've found one of the most practical ways to keep notes clean is a technique I call the Quote-Paraphrase-Summary method. Instead of mindlessly copying and pasting interesting lines, you actively engage with every single source. This forces a clear separation between the author's words, your interpretation of them, and your own big-picture takeaway.
Here’s how it works in practice:
- Quote: First, copy the original text word-for-word and wrap it in quotation marks. Right away, drop the full citation next to it. This is your raw material, cleanly captured.
- Paraphrase: Next, right below the quote, rewrite the concept entirely in your own words and sentence structure. This critical step ensures you're actually processing the information, not just echoing it.
- Summary/Your Idea: Finally, jot down a quick note on why this quote matters. How does it support your argument? What’s your unique take on it? This part is 100% your own thinking.
Using this simple three-part structure makes it nearly impossible to confuse a source's text with your own analysis later on.
By actively separating quotes from your own interpretations during the note-taking phase, you are building a firewall against accidental plagiarism. This structured approach makes it nearly impossible to mistakenly present borrowed ideas as your own when you begin writing.
Using Tools To Reinforce Your System
Your organizational system doesn't have to be some overly engineered, complex beast. It can be as simple as a well-structured document, a spreadsheet, or a dedicated reference manager. The only thing that matters is consistency.
This is where free tools like Zotero or Mendeley are absolute game-changers. They work like a digital library for all your sources, letting you store articles, highlight key passages, and attach notes in one central hub. Best of all, they automatically generate your citations and bibliographies in whatever style you need.
For example, you find a great PDF online. With one click, you can save it to Zotero, which instantly pulls all the bibliographic info—author, title, year, you name it. Then, you can highlight a key passage right in the PDF and attach your "Paraphrase" and "Summary" notes directly to that highlight.
When it's time to write, you have a beautifully organized set of notes and can drop perfectly formatted citations straight into your document. This transforms citation from a painful afterthought into a seamless part of your research process. This kind of proactive organization is the real secret to writing with integrity and confidence.
Mastering Paraphrasing to Make Ideas Your Own

Learning how to paraphrase properly is one of the most powerful skills you can build to avoid plagiarism. But it's so much more than that. It’s not about just swapping a few words around with synonyms.
True paraphrasing is about proving you understand an idea well enough to explain it in your own words and from your own perspective. It’s a way to filter information, connect it to your main argument, and add your own unique voice to the conversation.
A Four-Step Method for Paraphrasing That Actually Works
To do this right, you need a system. A good process forces you to break free from the original text's structure and truly make the idea your own.
Here's how I approach it every time:
- Read until you get it. Read the original passage until you fully grasp the meaning. Don't move on until you could explain the core idea to a friend without looking at the page.
- Put the source away. This is a non-negotiable step. Seriously. Close the book or the browser tab so you're not tempted to peek at the original wording.
- Write it in your voice. Now, write down the concept using your own words and sentence structure. Focus on getting the essential information down as you understand it.
- Compare and cite. Finally, open the original source again. Compare your version to the original to make sure you've kept the meaning accurate without borrowing the exact phrasing. This is also when you add your citation immediately. Don't wait.
Following these steps creates the mental distance you need to avoid "patchwriting," which is when you accidentally mimic the source too closely. It happens to the best of us, but this process helps prevent it.
Paraphrasing in Action: A Before-and-After
Let's look at a quick example to see the difference between a lazy attempt and a skillful paraphrase.
Original Text: "The rapid proliferation of digital communication technologies has fundamentally reshaped social interactions, leading to a decline in face-to-face engagement and fostering a culture of virtual connectivity."
A poor attempt just shuffles words around. It’s a classic mistake.
- Poor Paraphrase: "The quick growth of digital tech has changed social engagement, causing less in-person interaction and creating a culture of online connection."
See? It’s basically the same sentence with a few words swapped out. That’s still plagiarism.
Now, let's look at a strong paraphrase:
- Skillful Paraphrase: "As digital communication tools have become more common, people interact less in person and rely more heavily on virtual relationships to stay connected."
This version completely reworks the sentence and uses different words to express the same core idea. It shows genuine understanding.
Moving from Paraphrasing to Summarizing
Summarizing takes things a step further. Instead of just rephrasing a single idea or paragraph, you’re boiling down the main argument of an entire article or chapter into just a few sentences. This skill is crucial for showing you understand the big picture and how a source fits into your own work. And just like with paraphrasing, a summary always needs a citation.
If you’re struggling to find different ways to rephrase an idea, a tool like an AI Paraphraser can be a helpful resource for exploring new wording without losing the original meaning.
The demand for these kinds of tools is exploding. The plagiarism checker tool market was valued at around $0.22 billion and is on track to hit $0.56 billion by 2033. This growth shows just how much writers and institutions rely on technology to ensure work is original.
A Realistic Guide to Citing Your Sources
Citations can feel like a chore. All those rules, commas, and weird abbreviations. But let's look at them a different way. Think of them less as a penalty and more as showing your work. They're the backbone of any strong argument, giving credit where it's due and letting your readers see the intellectual trail you followed.
The principle is simple. If an idea, a statistic, a quote, or a chunk of data isn't yours, it needs a reference. That’s it.
The real goal here is to prove your points with solid evidence, show respect for other creators, and join the larger academic or professional conversation. Good citations signal that you’ve done your homework and are building on a foundation of real knowledge.
Understanding Citation Styles
You’re going to run into different citation styles, and the one you use will almost always depend on your field of study or where you're publishing. Don't get bogged down trying to memorize the tiny details of each one. Just understand their purpose and find a reliable tool or guide to handle the formatting for you.
Here’s a quick rundown of the big three:
- APA (American Psychological Association): You’ll see this everywhere in the social sciences, education, and psychology. APA puts a big emphasis on the date of publication because, in these fields, timeliness is everything.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): This is the go-to for the humanities—think literature, arts, and philosophy. It focuses on the author and page numbers, since the specific wording and where to find it are what matter most.
- Chicago (Chicago Manual of Style): Super flexible and used all over, especially in history. It gives you two options: a notes-and-bibliography system (common in humanities) or an author-date system (more for the sciences).
Honestly, the specific format is less important than the act of citing itself. These styles are just standardized ways to give credit. For a deeper dive into the ethics behind it, these academic integrity guidelines are a great resource for reinforcing good habits.
A Simple When-to-Cite Checklist
Not sure if something needs a citation? Just run through this quick mental checklist. If you answer "yes" to any of these, you need to add a reference. It’s a simple audit that can save you from a world of trouble later on.
Key takeaway: Citing sources isn't just about avoiding trouble; it's about building your own credibility. Every citation strengthens your work by showing it’s supported by established research, making your writing far more persuasive.
Does your work include any of the following?
- Direct quotes pulled word-for-word from another source?
- Statistics, numbers, or data from a report, study, or article?
- A specific theory, idea, or argument you learned from someone else?
- A summary or paraphrase of another person’s thoughts?
- Images, charts, or graphs you didn’t create yourself?
If you ever find yourself hesitating, just remember the golden rule: When in doubt, cite it. It is always, always better to over-cite than to leave a source uncredited and put your reputation on the line.
Using Tech as Your Final Quality Check
After you’ve done the heavy lifting—organizing your thoughts, paraphrasing sources, and citing everything correctly—it’s time for a final review. This is where technology becomes your last line of defense.
Think of plagiarism checkers as a safety net, not a magic wand. They’re fantastic tools for catching those accidental overlaps or forgotten citations that can slip past even the most careful writer. These platforms scan your text and compare it against a massive database of web pages, academic journals, and other published works. They then flag any passages that match other sources, giving you a chance to fix them before anyone else sees your work.
How to Make Sense of Plagiarism Reports
Here’s something to keep in mind: a high similarity score doesn't automatically mean you've plagiarized. It’s easy to panic when you see a high percentage, but don't. Plagiarism checkers often flag common phrases, properly cited quotes, and even your bibliography.
The key is to interpret the report intelligently. Look at what is being flagged, not just the overall percentage.
For instance, this is what the interface for Grammarly's Plagiarism Checker looks like. It helps you visualize exactly where the potential issues are.

The report shows you exactly which parts of your text might need another look. Your job is to use that feedback to refine your writing and make sure every borrowed idea is properly credited.
Popular Plagiarism Detection Tools
A few big names dominate this space, and each has its own strengths. You’ll probably run into one of these:
- Turnitin: This is the big one, used by countless universities. Turnitin is known for its incredibly deep academic database. Students often submit papers directly through it, giving instructors a detailed originality report.
- Grammarly: While most people know it for grammar and spelling, its premium version includes a powerful plagiarism checker. It scans against billions of web pages and academic databases, making it a great all-in-one tool for writers.
The market for these tools is exploding for a reason. Valued at around $1.2 billion, the global plagiarism detection software market is projected to more than double to $2.8 billion by 2033. This isn't just a trend; it's a clear signal that both education and business are serious about originality. If you're curious, you can read more about the market's growth and what's driving it.
AI and Its Role in Originality
The rise of AI writing tools adds a new wrinkle to this whole conversation. Let’s be clear: using an AI to write an entire essay and passing it off as your own is straight-up plagiarism. It completely misses the point of learning and misrepresents what you can do.
Crucial Insight: Technology is here to help you verify, not to write for you. Use it to check for accidental slip-ups and to polish your final draft, but never let it replace the real work of research, critical thinking, and original writing.
That said, AI can be an ethical partner in your writing process. It's a fantastic assistant for tasks like:
- Brainstorming ideas or exploring different angles on a topic you're stuck on.
- Summarizing dense research papers to help you get the main points before you put them into your own words.
- Outlining your thoughts to create a logical structure before you start writing.
Think of it as a research assistant, not the author. Running your final piece through a plagiarism checker is just one step in a much bigger process. To make sure your writing is truly polished from start to finish, our writing revision checklist can help you catch any other issues that might be hiding in your draft.
Of course. Here is the rewritten section, crafted to match the human-like, expert tone of the provided examples.
Your Burning Questions About Plagiarism, Answered
Even with the best intentions, the rules around plagiarism can feel murky. A few tricky scenarios pop up again and again, leaving writers unsure of what to do. Let's clear up some of that confusion.
Think of this as your go-to guide for navigating those gray areas with confidence.
Can I Plagiarize Myself?
Believe it or not, yes. It’s called self-plagiarism, and it happens when you reuse your own previously submitted or published work without permission. It’s a classic mistake—submitting the same essay for two different classes or lifting paragraphs from an old article for a new one.
Most universities and publishers have strict policies against this. The best practice? Always check the guidelines. If you want to build on your own past work, you absolutely must cite it, just as you would any other source.
Does Common Knowledge Need a Citation?
Usually, no. Common knowledge covers facts that are widely known and easily found in multiple general sources. Stating "Paris is the capital of France" or "The Earth revolves around the Sun" doesn't require a citation. They're undisputed, universally accepted facts.
But this is where the line can get a little blurry.
Here’s a good rule of thumb: if you had to look it up in a specific source, it probably isn’t common knowledge. When in doubt, just add the citation. It’s the safest way to protect your work and give proper credit.
How Different Does My Paraphrase Need To Be?
A real paraphrase is so much more than just swapping out a few words. To truly make an idea your own—and prove you actually understand it—you need to fundamentally change both the wording and the sentence structure.
Think of it like this: you absorb an idea, process it, and then explain it to someone in your own natural voice.
- Weak Paraphrasing: You keep the original sentence structure and just play "find-and-replace" with a few words. Plagiarism checkers spot this easily.
- Strong Paraphrasing: You completely rephrase the concept using your own unique sentence patterns. This shows you've genuinely grasped the material.
The goal isn't just to repeat information but to use it to build your own argument. It’s about transforming knowledge, not just telling it.
Is It Plagiarism if It's Accidental?
Yes, it's still plagiarism. Intent doesn't really matter—academic and professional standards hold you responsible for everything you write. A forgotten citation or a clumsy paraphrase that stays too close to the original can land you in the same hot water as deliberate copying.
This is exactly why good habits are non-negotiable. Meticulous note-taking and using a plagiarism checker as a final safety check are your best friends. They catch those honest mistakes before they turn into serious problems.
Ready to ensure your writing is polished, original, and sounds completely human? Natural Write transforms AI-generated text into seamless, natural language that bypasses AI detectors with ease. Perfect your essays, blogs, and professional content with one click. Try it now at Natural Write.


